Discover what is video transcoding and how this invisible process enables seamless streaming. A clear guide to the technology powering modern media.
In This Article
Subscribe to our newsletter
Ever wonder how you can start watching a show on your TV, pick it up on your phone during your commute, and then finish it on your laptop without a single hiccup? That seamless experience is all thanks to a process working tirelessly behind the scenes: video transcoding.
Think of it as a universal translator for your video files. It’s the hidden engine that makes sure a single video can play perfectly on any device, no matter its screen size, processing power, or your internet speed.
The Hidden Engine Behind Modern Video Streaming
When a studio creates a movie, they start with a massive, ultra-high-quality master file. But that master file is way too big and clunky for your iPhone to handle. That's where transcoding comes in.
It takes that one master file and intelligently creates multiple, optimized versions. Each version is tailored for a specific scenario—a smaller, lower-bitrate version for mobile viewing on a shaky connection, a high-definition one for your smart TV, and everything in between. Without it, media teams would have to manually create and store dozens of separate files for every single video, a workflow that’s as inefficient as it is expensive.
This infographic gives you a great visual of how one source file gets remixed for every screen.
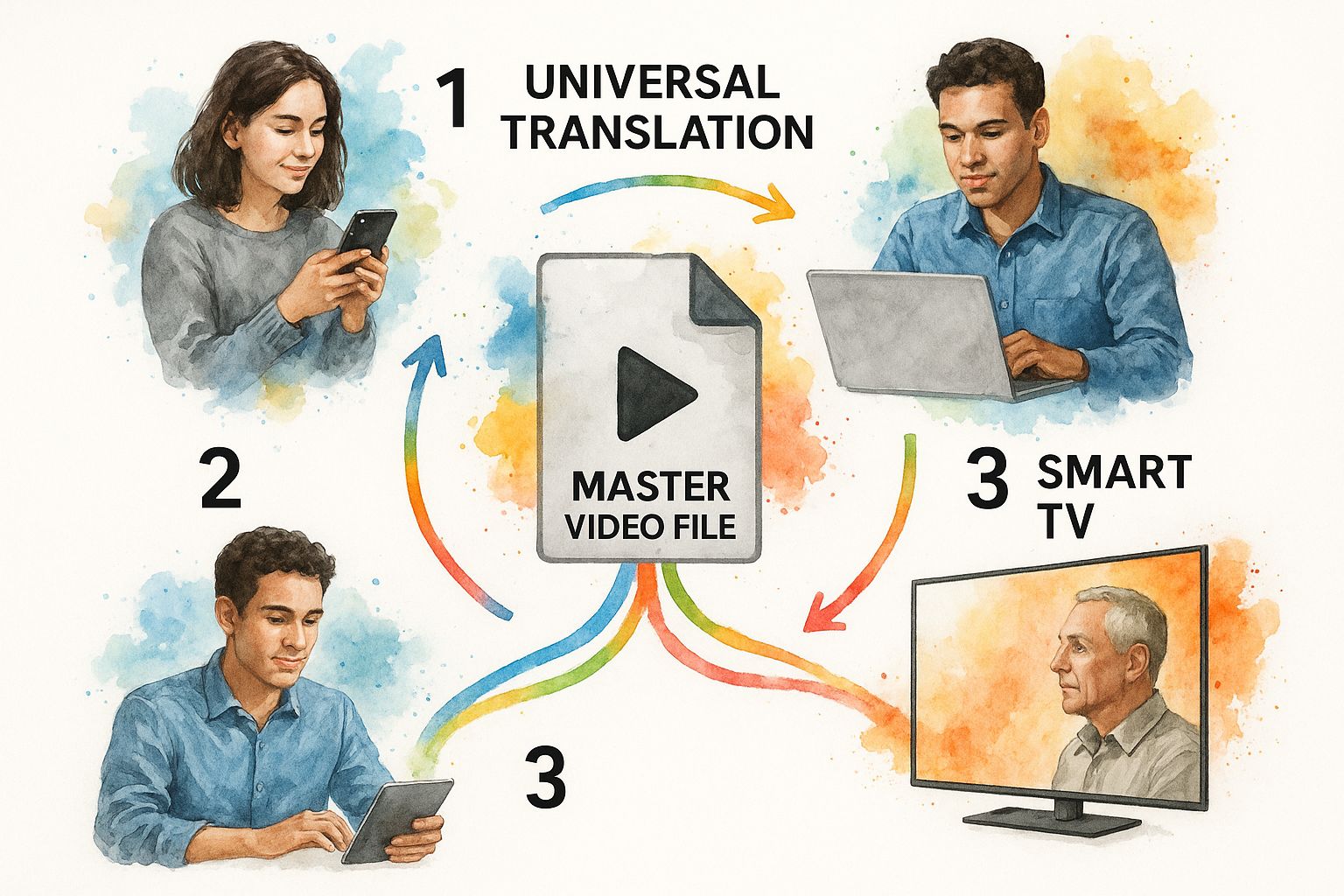
As you can see, the core idea is simple: take one, give back many. It’s all about creating tailored streams that guarantee a smooth, consistent user experience no matter where or how your audience is watching.
At its core, video transcoding is about accessibility and efficiency. It breaks down compatibility barriers, allowing content to reach the widest possible audience with the best possible quality for their specific connection.
The numbers back this up. The global video transcoding market is on a rocket ship, projected to jump from USD 9.5 billion in 2024 to over USD 27.49 billion by 2031. This explosive growth shows just how crucial it is for managing the world's tsunami of video content.
Of course, transcoding is just one piece of a much larger puzzle. Many of these complex processes can be automated to make life easier, and you can learn more about how to boost production efficiency with media workflow automation.
To see it in action, just look at live TV streaming, an experience that simply couldn't exist without fast, reliable video transcoding working in real time.
How Video Transcoding Works Step by Step
To get your head around video transcoding, think of it like packing a suitcase for different trips. You don't just throw the same stuff in whether you're going to the beach or on a ski trip, right? The process boils down to two key stages: decoding (unpacking) and encoding (repacking). It's a clever method for making sure your video is perfectly prepped for any destination.
First, your original video file—your fully packed suitcase—is decoded. This step unpacks the compressed file into its raw, unadulterated components. It’s like opening the suitcase and laying everything out on the bed: the individual video frames (the clothes), the audio streams (the shoes), and the metadata (your passport and travel documents). At this point, everything is in a universal, uncompressed state, ready to be rearranged.

The Repacking Phase: Encoding
Next up is the encoding stage, which is where the real magic happens. Here, all those raw components are strategically repacked into a brand-new suitcase—a new file format. This is our chance to make critical adjustments based on the final destination and the journey it'll take to get there.
This involves tweaking a few key settings:
- Codec: This is the compression algorithm. Think of it as choosing your packing method—rolling vs. folding. You might stick with the universally accepted H.264 or opt for a newer, more efficient one like AV1 to get better quality into a smaller file.
- Bitrate: This controls how much data is used for each second of video. A higher bitrate means better quality but a bigger file (your oversized luggage), while a lower bitrate is perfect for viewers on slower connections.
- Resolution: These are the video's dimensions, like 1080p or 4K. Transcoding lets you create smaller versions (like 480p) for people watching on their phones.
By carefully adjusting these parameters, a single 4K master file can be repacked into dozens of optimized versions. This is how a viewer on a blazing-fast 5G connection gets a gorgeous 1080p stream on their new iPhone, while someone on spotty public Wi-Fi still gets a smooth, buffer-free 480p version. For a deeper dive into this balancing act, check out our guide on how to compress videos and keep quality.
The goal of transcoding isn't just to change a file's format; it's to create the best possible viewing experience for every single user by adapting the video to their specific context.
Modern transcoding workflows lean heavily on specialized hardware to speed things up. Having the right GPU makes a world of difference, so it pays to understand what makes for the best graphics card for video editing. As new standards like H.265 and AV1 become more common, powerful hardware is essential for processing massive video libraries efficiently for everything from on-demand streaming to live video calls.
Why Transcoding Is a Non-Negotiable for Modern Media
Knowing what transcoding is is one thing, but seeing how it directly impacts your bottom line is what really matters. Let’s be blunt: without it, reaching a global audience in today’s chaotic device market would be a nightmare.
It all boils down to three critical areas that make or break your user experience and operational budget.
First up is achieving universal device compatibility. Imagine this: you upload a single, high-quality master file. Instantly, it’s ready to play flawlessly on an iPhone in New York, an Android tablet in Tokyo, and a smart TV in London. That’s the magic of transcoding. It creates a whole family of optimized files from your original, making sure your content looks perfect on any screen, no matter the OS or hardware.
Enabling a Buffer-Free Experience
The second big win is unlocking adaptive bitrate streaming (ABS). This is the secret sauce that powers platforms like Netflix and YouTube, giving viewers that smooth, uninterrupted experience we all expect.
Here’s how it works. ABS technology lets the video player on a viewer's device check their internet connection in real-time. If the connection is solid, it pulls down a high-quality, high-bitrate stream. But if the Wi-Fi suddenly gets spotty, it instantly switches to a lower-quality version to avoid that dreaded buffering wheel.
Transcoding is what creates this "ladder" of different quality versions, giving the player a whole menu of options to choose from. Without that range of transcoded files, adaptive streaming simply can't exist.
Optimizing Costs and Delivery
Finally, transcoding is a massive lever for optimizing storage and delivery costs. Your high-resolution master files are huge. They’re expensive to store and even more expensive to ship across the internet. By creating smaller, more efficient versions of that file, you can slash your cloud storage bills and your content delivery network (CDN) bandwidth fees.
This efficiency is absolutely vital for the exploding over-the-top (OTT) market. As streaming services expand globally, they need to deliver quality video to viewers on all kinds of networks, from fast fiber to shaky mobile connections. As you can see in these video transcoding market insights, efficiently managing file sizes is the key to scaling sustainably. It’s how you serve millions of viewers without letting your costs spiral out of control.
See Video Transcoding in Real-World Scenarios
The theory is one thing, but seeing transcoding in action is where you really grasp its power. This process is the invisible engine humming behind the world's biggest video platforms, making the digital media we consume every day even possible. Let's look at a couple of examples you’re probably already familiar with.

Streaming Services and OTT Platforms
Ever wonder how giants like Hulu or Disney+ do it? When they get a new movie, it arrives as a single, enormous master file. Their challenge is to get that movie to millions of subscribers at the exact same time, all watching on different gadgets—from 4K smart TVs to older phones—with internet speeds that are all over the map.
This is where massive transcoding farms come into play. These powerful systems grab that one master file and churn out a whole spectrum of versions, known as a "bitrate ladder." This ensures the person with a blazing-fast fiber connection gets that stunning 4K HDR stream, while someone on a shaky mobile network still gets a smooth, buffer-free show at a lower resolution. It just works.
For OTT platforms, transcoding isn’t just a technical step; it’s the core of their business model. It guarantees a premium, reliable viewing experience that keeps subscribers coming back for more, no matter how or where they watch.
User-Generated Content Platforms
Now, think about platforms like YouTube and TikTok, which are drowning in a constant flood of user-generated content (UGC) every single minute. People upload videos from thousands of different devices in a dizzying array of formats, codecs, and resolutions. Without some kind of automated system, it would be total chaos.
Automated transcoding pipelines are the only way to manage this. The second a video is uploaded, it's whisked away to a transcoding service. This service takes that unpredictable user file and instantly converts it into a standardized set of formats that will play on pretty much any device on the planet.
This is how every video, whether it was shot on a pro-grade camera or a ten-year-old phone, becomes instantly watchable for a global audience. The sheer scale is mind-boggling, demanding incredibly efficient transcoding to handle that endless firehose of new content without a single hiccup.
Choosing the Right Video Transcoding Workflow
Once you get a handle on what video transcoding can do, the next logical question is: how do we actually do it? The right answer really depends on your team's budget, technical know-how, and what your projects demand.
For the most part, you've got three main roads you can go down.
On-Premise Solutions
Going on-premise means you buy, set up, and maintain your own hardware encoders right in your own facility. This approach gives you the ultimate control over security and the entire process, which is a non-negotiable for organizations with ironclad data policies.
The trade-off? It’s a serious upfront investment. You're not just buying the gear; you also need a dedicated technical team to keep it running, updated, and to fix it when things break. Plus, your ability to scale is literally limited by the number of machines you own. If a huge project lands on your desk unexpectedly, you can't just magically conjure more processing power.
Cloud-Based Services
On the flip side, cloud-based services have become the default for most modern media teams, and for good reason. Platforms like AWS Elemental MediaConvert deliver unbelievable flexibility without the hardware headaches.
Instead of sinking capital into machines that will eventually become obsolete, you operate on a pay-as-you-go model. You only pay for the processing you actually use. This is a game-changer for businesses with fluctuating workloads—you can ramp up for a massive launch one week and dial it way back the next. If you're getting your files ready for the cloud, it's worth learning more about how to optimize video for web performance.
The biggest win with the cloud is agility. It completely removes the burden of managing hardware and lets your team pour their energy into creating amazing content, not maintaining infrastructure. You get access to world-class transcoding tech without the sticker shock.
The Hybrid Model
Finally, there’s the hybrid model, which, just as it sounds, cherry-picks the best of both worlds. A company might keep its most sensitive, high-stakes transcoding jobs on-premise for maximum security, but then push overflow work or less critical tasks to the cloud.
This gives you a balanced solution—the tight control of on-premise hardware combined with the on-demand scalability of the cloud. It’s all about tailoring the workflow to your specific business needs.
Got Questions About Video Transcoding? We’ve Got Answers.
As you start working more with video, it’s only natural for a few questions to pop up about transcoding. It's a process that sounds technical, but the core ideas are pretty straightforward once you break them down.
Let's clear up some of the common questions we hear from media teams.
Is Transcoding the Same as Encoding?
Not quite, but they're definitely related. Think of encoding as the first step: taking raw video footage and compressing it into a digital file for the first time, like an MP4.
Transcoding, on the other hand, takes a file that’s already been encoded and converts it to a new format or a different set of specs.
Here’s a simple analogy:
- Encoding: You write a book in English.
- Transcoding: You translate that English book into Spanish, French, and German so more people can read it.
At its core, transcoding is a two-step dance: a file is first decoded back to an uncompressed state and then re-encoded with new settings.
Does Transcoding Reduce Video Quality?
The short answer is yes, it can. But it’s not a bad thing—it’s usually the whole point.
Transcoding is a "lossy" process, meaning a little bit of data is intentionally discarded every time a file gets re-compressed. The goal isn’t to make your video look bad; it's to make it smaller and more efficient for different playback scenarios.
A smart transcoding workflow is all about striking the right balance. You want to shrink the file size enough for smooth streaming on a weak connection, but not so much that the quality drop is jarring.
The art of good transcoding lies in finding that sweet spot between file size and visual fidelity. After all, the highest quality video in the world doesn’t matter if your audience is stuck staring at a buffering wheel.
Why Not Just Use One Standard Video Format for Everything?
If only it were that simple! In a perfect world, one format would rule them all, but the reality of our digital world is fragmentation. We have thousands of different devices, from brand-new 8K smart TVs to decade-old smartphones, all with different screen sizes, operating systems, and processing power.
That shiny 4K file that looks incredible on a new TV would bring an older phone to a grinding halt.
Transcoding is the great equalizer. It creates different versions of the same video, a process known as creating an adaptive bitrate ladder. This ensures that no matter what device or internet connection someone has, they automatically get served a version of the video that’s a perfect fit for their screen and bandwidth. It's the secret sauce behind a consistently smooth playback experience for everyone.
To give you a quick reference, here are some of the most common questions and their direct answers.
Frequently Asked Questions
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is video transcoding? | It’s the process of converting an existing digital video file from one format to another (e.g., MOV to MP4) or changing its specifications (e.g., 4K to 1080p). |
| Is transcoding different from encoding? | Yes. Encoding is the initial conversion of raw video into a compressed file. Transcoding takes an already encoded file and re-converts it. |
| Why is transcoding necessary? | To ensure your video can play smoothly on a wide variety of devices, browsers, and internet connections, providing a good user experience for everyone. |
| Does transcoding hurt video quality? | It can, as it's a "lossy" process. However, the goal is to strategically reduce file size while maintaining the best possible quality for a given delivery context. |
| What are some common transcoding use cases? | Creating multiple resolutions for adaptive bitrate streaming, converting files for social media platforms, and making broadcast-ready files. |
Hopefully, this clears things up! Understanding these fundamentals is key to building a video workflow that actually works.
Ready to stop wrestling with complex video workflows? Aeon uses AI to automatically transform your existing content into engaging, ready-to-publish videos, handling all the technical details so you can focus on your message. Discover how Aeon can scale your video creation today.


.jpg)